diabetic gastroparesis

You may already have experienced some of the effects of DGP in your life, but what is diabetic gastroparesis? Once you’ve read this page, you’ll have greater understanding of the following:
What is gastroparesis?
Also known as delayed gastric emptying, gastroparesis happens when the muscles that help move food along the digestive tract don’t work properly. With gastroparesis, you may experience “slow stomach," where food and medications stay in the stomach for a long time before emptying into the small intestine.1 When delayed gastric emptying occurs, it can lead to nausea, bloating, feeling full after eating only a small amount, stomach pain, and vomiting.2
means
stomach.
is the Greek word
for paralyzed.
you get "gastroparesis," or
"paralyzed stomach,"
which accurately describes this condition.

It is estimated that 20%-40% of people with diabetes will develop gastroparesis.3

What is diabetic gastroparesis?
DGP is a chronic condition that can happen to people who have diabetes. If you have DGP, you know all about how it can impact your digestive system and disrupt your day-to-day life. Although there is no cure for DGP, there are things you can do to help manage your symptoms.4 See tips.
What causes DGP?
DGP is often related to nerve damage that is caused by diabetes. When the nerves that are responsible for moving through the stomach and promoting stomach emptying are damaged, they cannot work efficiently and can lead to DGP symptoms.5
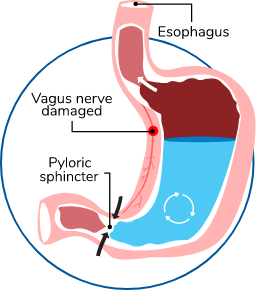
Who is at risk for DGP?
People who have type 1 or type 2 diabetes can get diabetic gastroparesis.
However, people who have type 1 diabetes are at a higher risk.6

Although women are4Xmore likely to get DGP, it is not uncommon for men to develop it, too.6,7
What are the potential effects of DGP?
Gastroparesis symptoms can make life challenging for many people. If not managed, these symptoms can have a range of negative effects on physical and mental health, such as5,6,8-10:
- Extreme swings in blood sugar and difficulty managing diabetes, which can lead to other complications
- Poor nutrition and dehydration
- Emergency room visits and hospitalizations
- Difficulty participating in social activities like school or work
- Depression and anxiety
Nausea and vomiting may make it difficult to take and keep down oral medications. Learn more about symptoms

Patients with DGP have more emergency room visits and longer hospital stays than patients with other forms of gastroparesis.8
Reference: 1. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Definition & facts for gastroparesis. https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/gastroparesis/definition-facts. Accessed June 11, 2021. 2. Camilleri M, Parkman HP, Shafi MA, Abell TL, Gerson L. Clinical guideline: management of gastroparesis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2013;108(1):18-37. 3. Saljoughian M. A new approach to managing gastroparesis. US Pharm. 2019;44(2):32-34. 4. Sadiya A. Nutritional therapy for the management of diabetic gastroparesis: clinical review. Diabetes, Metab Syndr Obes.2012;5:329-335. 5. Krishnasamy S, Abell TL. Diabetic gastroparesis: principles and current trends in management. Diabetes Ther. 2018;9(Suppl 1):1-42. 6. Bharucha AE. Epidemiology and natural history of gastroparesis. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2015;44(1):9-19. 7. Jung HK, Choung RS, Locke GR III, et al. The incidence, prevalence and outcomes of patients with gastroparesis in Olmsted County, Minnesota from 1996 to 2006. Gastroenterology. 2009:136(4):1225-1233. 8. Dudekula A, O’Connell M, Bielefeldt K. Hospitalizations and testing in gastroparesis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011;26(8):1275-1282. 9. Hirsch W, Nee J, Ballou S, et al. Emergency department burden of gastroparesis in the United States, 2006-2013. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2019;53(2):109-113. 10. The NIDDK Gastroparesis Clinical Research Consortium. Factors related to abdominal pain in gastroparesis: contrast to patients with predominant nausea and vomiting. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2013;25(5):427-438.
What is Gimoti® (metoclopramide) nasal spray?
GIMOTI is a prescription medicine used 30 minutes before meals and at bedtime for 2 to 8 weeks to relieve symptoms of slow stomach emptying in adults with diabetes. Avoid treatment with metoclopramide (all dosage forms and routes of administration) for longer than 12 weeks.
GIMOTI is not recommended for use in children under age 18.
Important facts about GIMOTI
This is a summary of important information you need to know about GIMOTI. This information does not take the place of talking with your healthcare professional about your medical condition or your treatment.
What is the most important information I should know about GIMOTI?
GIMOTI can cause serious side effects, including: TARDIVE DYSKINESIA: Abnormal muscle movements, mostly of the face or tongue muscles. You cannot control these movements, and they may not go away even after stopping GIMOTI. Your chances of getting tardive dyskinesia increase
- The longer you take metoclopramide and the more metoclopramide you take. You should not take GIMOTI for more than 8 weeks at a time, and you should not take products containing metoclopramide (including GIMOTI) for more than 12 weeks at a time.
- If you are older, especially if you are an older woman (e.g., age 65 years and older)
- If you have diabetes
Call your healtcare professional right away if you get movements you cannot stop or control, such as lip smacking, chewing, or puckering up your mouth; frowning or scowling; sticking out your tongue; blinking and moving your eyes; shaking of your arms and legs.
Do not use GIMOTI if you
- Have a history of tardive dyskinesia or have a problem controlling your muscles and movements after taking GIMOTI or a medicine that works like GIMOTI
- Have stomach or intestinal problems that could get worse with GIMOTI, such as bleeding, blockage, or a tear in the stomach or bowel wall
- Have a type of tumor that can cause high blood pressure, such as pheochromocytoma
- Have epilepsy (seizures)
- Are allergic to metoclopramide. Stop taking GIMOTI right away and get emergency help if you have any of these symptoms:
- swelling of your tongue, throat, lips, eyes, or face
- trouble swallowing or breathing
- skin rash, hives, sores in your mouth, or skin blisters
Before starting GIMOTI, tell your healthcare professional about all your medical conditions, especially if you have
- Problems controlling your muscle movements after taking any medicine
- Parkinson’s disease
- Pheochromocytoma
- Kidney or liver disease
- Depression or mental illness
- High blood pressure
Also tell your healthcare professional if you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant, are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed, or drink alcohol.
Tell your healthcare professional about all the medicines you take, including prescription drugs and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
Speak with your healthcare professional before you start or stop any other medicines.
Especially tell your healthcare professional if you take
- Another medicine that contains metoclopramide, such as REGLAN® tablets
- Medicine for Parkinson’s disease
- Blood pressure medicine
- Medicine for depression, especially a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI)
- Antipsychotic medicine used to treat mental illness, such as schizophrenia
- Insulin
- Medicines that can make you sleepy, such as anxiety medicines, sleep medicines, and narcotics
What should I avoid while taking GIMOTI?
- Do not drink alcohol while taking GIMOTI
- GIMOTI may cause sleepiness or dizziness. Do not drive, operate machinery, or do potentially dangerous activities until you know how GIMOTI affects you
What are other possible side effects of GIMOTI?
- Other changes in muscle control and movement, such as:
- uncontrolled spasms of your face and neck muscles, or muscles of your body, arms, and legs (dystonia)
- parkinsonism – slight shaking, body stiffness, and trouble moving or keeping your balance
- being unable to sit still or feeling that you need to move your hands, feet, or body (akathisia)
- Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS) – a very rare but very serious condition. NMS can lead to death and must be treated in a hospital
- Depression, thoughts about suicide, and suicide
- High blood pressure
- Too much body water
- Increased prolactin
Call your healthcare professional and get medical help right away if you
- Feel depressed or have thoughts about hurting or killing yourself
- Have high fever, stiff muscles, problems thinking, very fast or uneven heartbeat, and/or increased sweating
- Have muscle movements that you cannot stop or control
- Have muscle movements that are new or unusual
The most common side effects of GIMOTI include
- Unpleasant taste after dosing
- Headache
- Tiredness
These are not all the possible side effects of GIMOTI. Ask your healthcare professional for medical advice about side effects.
You may report side effects related to Evoke Pharma products by calling 1-833-4-GIMOTI (1-833-444-6684) or emailing GIMOTImedinfo@evokepharma.com. If you prefer to report these to the FDA, either visit www.FDA.gov/medwatch or call 1-800-FDA-1088.
This information should not take the place of you talking with your doctor or healthcare professional. If you have any questions about your condition, or if you would like more information about GIMOTI, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. Only you and your healthcare professional can decide if GIMOTI is right for you.
Please see complete Prescribing Information, including Boxed Warning, Medication Guide, and Instructions for Use.
What is Gimoti® (metoclopramide) nasal spray?
GIMOTI is a prescription medicine used 30 minutes before meals and at bedtime for 2 to 8 weeks to relieve symptoms of slow stomach emptying in adults with diabetes. Avoid treatment with metoclopramide (all dosage forms and routes of administration) for longer than 12 weeks.
GIMOTI is not recommended for use in children under age 18.
Important facts about GIMOTI
This is a summary of important information you need to know about GIMOTI. This information does not take the place of talking with your healthcare professional about your medical condition or your treatment.
What is the most important information I should know about GIMOTI?
GIMOTI can cause serious side effects, including: TARDIVE DYSKINESIA: Abnormal muscle movements, mostly of the face or tongue muscles. You cannot control these movements, and they may not go away even after stopping GIMOTI. Your chances of getting tardive dyskinesia increase
- The longer you take metoclopramide and the more metoclopramide you take. You should not take GIMOTI for more than 8 weeks at a time, and you should not take products containing metoclopramide (including GIMOTI) for more than 12 weeks at a time.
- If you are older, especially if you are an older woman (e.g., age 65 years and older)
- If you have diabetes
Call your healthcare professional right away if you get movements you cannot stop or control, such as lip smacking, chewing, or puckering up your mouth; frowning or scowling; sticking out your tongue; blinking and moving your eyes; shaking of your arms and legs.
Do not use GIMOTI if you
- Have a history of tardive dyskinesia or have a problem controlling your muscles and movements after taking GIMOTI or a medicine that works like GIMOTI
- Have stomach or intestinal problems that could get worse with GIMOTI, such as bleeding, blockage, or a tear in the stomach or bowel wall
- Have a type of tumor that can cause high blood pressure, such as pheochromocytoma
- Have epilepsy (seizures)
- Are allergic to metoclopramide. Stop taking GIMOTI right away and get emergency help if you have any of these symptoms:
- swelling of your tongue, throat, lips, eyes, or face
- trouble swallowing or breathing
- skin rash, hives, sores in your mouth, or skin blisters
Before starting GIMOTI, tell your healthcare professional about all your medical conditions, especially if you have
- Problems controlling your muscle movements after taking any medicine
- Parkinson’s disease
- Pheochromocytoma
- Kidney or liver disease
- Depression or mental illness
- High blood pressure
Also tell your healthcare professional if you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant, are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed, or drink alcohol.
Tell your healthcare professional about all the medicines you take, including prescription drugs and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
Speak with your healthcare professional before you start or stop any other medicines.
Especially tell your healthcare professional if you take
- Another medicine that contains metoclopramide, such as REGLAN® tablets
- Medicine for Parkinson’s disease
- Blood pressure medicine
- Medicine for depression, especially a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI)
- Antipsychotic medicine used to treat mental illness, such as schizophrenia
- Insulin
- Medicines that can make you sleepy, such as anxiety medicines, sleep medicines, and narcotics
What should I avoid while taking GIMOTI?
- Do not drink alcohol while taking GIMOTI
- GIMOTI may cause sleepiness or dizziness. Do not drive, operate machinery, or do potentially dangerous activities until you know how GIMOTI affects you
What are other possible side effects of GIMOTI?
- Other changes in muscle control and movement, such as:
- uncontrolled spasms of your face and neck muscles, or muscles of your body, arms, and legs (dystonia)
- parkinsonism – slight shaking, body stiffness, and trouble moving or keeping your balance
- being unable to sit still or feeling that you need to move your hands, feet, or body (akathisia)
- Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS) – a very rare but very serious condition. NMS can lead to death and must be treated in a hospital
- Depression, thoughts about suicide, and suicide
- High blood pressure
- Too much body water
- Increased prolactin
Call your healthcare professional and get medical help right away if you
- Feel depressed or have thoughts about hurting or killing yourself
- Have high fever, stiff muscles, problems thinking, very fast or uneven heartbeat, and/or increased sweating
- Have muscle movements that you cannot stop or control
- Have muscle movements that are new or unusual
The most common side effects of GIMOTI include
- Unpleasant taste after dosing
- Headache
- Tiredness
These are not all the possible side effects of GIMOTI. Ask your healthcare professional for medical advice about side effects.
You may report side effects related to Evoke Pharma products by calling 1-833-4-GIMOTI (1-833-444-6684) or emailing GIMOTImedinfo@evokepharma.com. If you prefer to report these to the FDA, either visit www.FDA.gov/medwatch or call 1-800-FDA-1088.
This information should not take the place of you talking with your doctor or healthcare professional. If you have any questions about your condition, or if you would like more information about GIMOTI, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. Only you and your healthcare professional can decide if GIMOTI is right for you.
Please see complete Prescribing Information, including Boxed Warning, Medication Guide, and Instructions for Use.
